Tesla Superchargers vs Other EV Charging Networks: How Do They Compare?
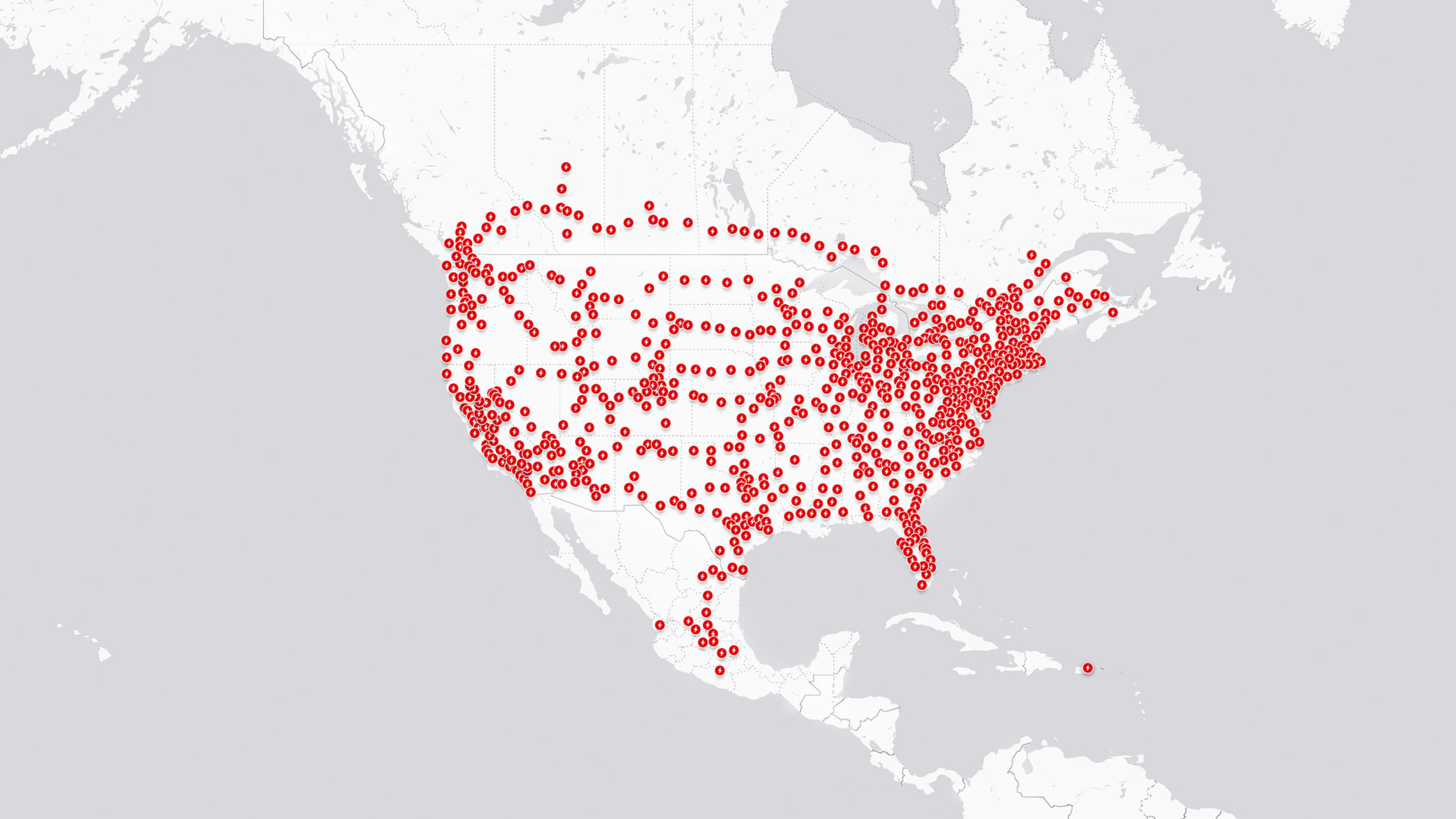
Electric vehicles are growing in popularity, but charging infrastructure remains a key factor for widespread adoption. For Tesla owners, the Supercharger network provides exclusive access to fast, convenient charging stations as you can see in the picture above which is from Tesla's website. But how does Tesla's network stack up against charging options for non-Tesla EVs? This article will compare the Tesla Supercharger network with other major charging networks in North America.
Tesla Supercharger Network
Tesla's proprietary Supercharger network consists of over 3,000 fast charging stations globally, with over 1,000 across the United States and Canada. Supercharger stations contain multiple charging stalls and are strategically placed along major highways and thoroughfares to enable long distance EV travel.
The Supercharger network uses DC fast charging technology exclusively. Most Supercharger stalls deliver 72-250kW charging, enabling rapid charging speeds. In ideal conditions, they can add up to 200 miles of charge in just 15 minutes. Tesla has also rolled out V3 Superchargers capable of up to 250kW charging for maximum charging velocity.
Supercharger stations are conveniently located near restaurants, shopping centers, and rest stops. They often have lounge areas with amenities like restrooms, WiFi, and refreshments. Tesla provides real-time Supercharger availability within their vehicle GPS systems and mobile app.
Importantly, Supercharger access is included with all Tesla vehicles. Tesla owners can charge their EVs for free at Supercharger stations. This helps alleviate range anxiety and provides freedom for long distance travel. Tesla continues to aggressively expand the network, especially in high-demand areas.
Third-Party EV Charging Networks
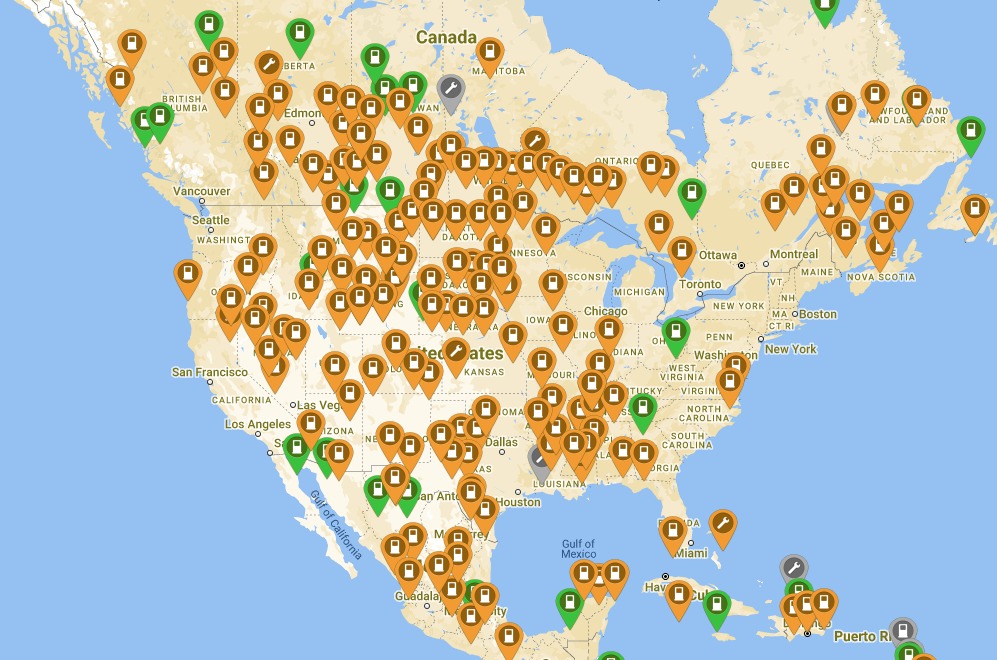
For non-Tesla EV drivers, several third-party charging networks exist across North America. Each network employs different business models and charging speeds. As you can see in the picture above from plugshare.com these networks combined with other chargers combine to provide a considerable amount of charging locations for people driving Kias, Rivians, Polestars, Fords or other vehicles. The major networks include:
Electrify America
The largest non-Tesla network was established by Volkswagen as part of their diesel emissions settlement. It has over 800 charging stations with 3,500+ DC fast charging stalls planned by the end of 2025. Electrify America locations feature 150kW-350kW ultra-fast charging for speeds up to 20 miles per minute.
Charging pricing is by kWh used instead of time occupied. Membership plans with discounted charging rates are available but not required. The network is open to all EVs with the appropriate charging standard. Locations tend to be along high-traffic routes and metro areas. An app shows station availability.
EVgo
EVgo operates the largest public US fast charging network with over 1,500 stations and 10,000+ Level 2/DC fast charging ports across 34 states. Their DC fast chargers are 50kW-350kW capable of adding 60+ miles of range in 15 minutes.
EVgo has a membership model with monthly charging packages for frequent users. Guest rates are $0.31-$0.79 per minute depending on region. EVgo mainly locates stations in urban areas for intracity charging. Their app provides charging availability and reservation capability.
ChargePoint
ChargePoint has the world’s largest EV charging network by total ports available. They have 13,000+ Level 2 AC and DC fast charging spots at over 2,000 locations in North America.
Pricing is determined by each charging station owner/operator. Both pay-per-session and monthly network access plans are available. Charging speeds max out at around 50kW, slower than newer DC fast chargers. Locations are widespread across the United States and Canada.
Volta Charging
Volta’s business model is unique - they offer free EV charging sponsored by on-site business partners, from retailers to entertainment venues. Their stations feature large digital displays for ads and content.
Volta has over 3,000 charging ports in over 850 locations in the US. Charging is limited to Level 2 speeds with typical rates of 18 miles of range per hour. While slower than DC fast charging, it can provide substantial free charging for Volta users.
Tesla vs Other Networks: Pros and Cons
Tesla Owners
For Tesla drivers, the Supercharger network provides unparalleled access to fast, convenient charging with no fees. The rapid expansion of the network enables true long distance travel. Tesla's integrated trip routing based on Supercharger locations makes charging simple and efficient on the go.
However, reliance on Superchargers also means Tesla drivers can't access thousands of third-party charging locations. Long Supercharger lines and wait times are also a growing concern as the Tesla fleet expands. Still, the Supercharger network remains a major perk of Tesla ownership.
Non-Tesla Owners
The benefit for non-Tesla EV owners is the ability to leverage multiple charging networks. Apps like PlugShare aggregate stations across networks for maximum charging access. This provides more flexibility and charging redundancy if one network has outages or busy stations.
The downside is non-uniform charging experiences across networks. Pricing models, charging speeds, locations, memberships vary widely. Having to maintain accounts across multiple networks also adds complexity compared to Tesla’s seamless proprietary stations.
Direct comparisons:
Speed - Tesla Superchargers are still the fastest widely available DC fast charging option. But ultra-fast 350kW options from Electrify America and others are catching up.
Convenience - Tesla's integrated network with real-time availability and trip planning is more seamless. But third-party apps are improving the charging experience across networks.
Accessibility - Tesla exclusivity means limited locations. Third-party networks provide more geographic flexibility and redundancy.
Cost - Supercharger access is free for Tesla owners. Third-party networks have fees, though membership plans help frequent drivers.
Future Outlook
As EV adoption grows, charging infrastructure must keep pace. Tesla is expanding Superchargers to maintain exclusive advantages for their owners. Meanwhile, third-party networks are racing to deploy reliable ultra-fast DC fast charging to attract all EV drivers.
Apps and payment integration across networks will help improve non-Tesla driver experiences. But the Supercharger network’s convenience and free charging for Tesla remains a big strategic asset. Ultimately, expanding reliable fast charging for all EVs will be critical to mainstream adoption.
It is also important to consider for non-Tesla EV drivers, access to charging networks depends on the charging standards supported by their vehicles. While many new EVs like Rivian trucks can utilize networks like Electrify America, EVgo, and ChargePoint, some charging incompatibility still exists across brands. For example, Tesla uses its own proprietary connector which requires an adapter to use other networked chargers. EV owners must check compatibility for the charging networks in their regions and along planned travel routes for seamless public charging access. For more information about charging stations (other than Tesla) check out plugshare.com.